

The gate oxide thickness of the transistor is 8 angstroms, or roughly three atomic layers of silicon dioxide between the polysilicon gate electrode and the silicon channel. By then, extreme ultraviolet lithography could be used along with 157-nm optical lithography tools, Chau said.Īt the Kyoto workshop, Chau updated Intel's progress on the 30-nm transistor. The transistor with a 20-nm gate length discussed at the Nanoelectronics Workshop corresponds to the 45-nm technology node, which is expected to go into volume manufacturing in 2007. That transistor will be used in the 0.065-micron (65-nanometer) technology node, which is expected to come into manufacturing in 2005, according to the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors. Equally important is a less-often-discussed historical trend the halving of the cost per transistor with each new technology generation.Īt last year's International Electron Devices Meeting in San Francisco, Intel presented a transistor with a gate length of 30 nanometers. But Intel has publicly rejected those approaches and said they will be unnecessary for the foreseeable future.Ī 30 percent shrink in transistor size will bring a 30 percent gain in transistor performance, without resorting to more complex processes or device structures, Chau said. Other chip makers, most visibly IBM Microelectronics, have argued that performance gains from CMOS scaling are slowing, which will require a shift to silicon on insulator (SOI), to strained silicon, or perhaps to double-gated device structures. In a keynote speech delivered Sunday (June 10) at the Silicon Nanoelectronics workshop here, Robert Chau, director of transistor research at Intel's components research group in Hillsboro, Ore., cited Intel's belief that planar CMOS transistors will carry it through the rest of this decade. But the transistor indicates the scalability of planar CMOS in terms of transistor size, voltage and speed. Intel has implemented a 20-nm NMOS transistor but has yet to make a PMOS version, which would be needed to create CMOS circuits. researchers have provided a peek at a transistor with a gate length measuring just 20 nanometers, which Intel expects to put into production in 2007 when its microprocessors hold a billion transistors and hit speeds of 20 GHz. The 180 nm CMOS process was later commercialized by TSMC in 1998, and then Fujitsu in 1999.KYOTO, Japan Intel Corp. In 1988, an IBM research team led by Iranian engineer Bijan Davari fabricated a 180 nm dual-gate MOSFET using a CMOS process. In 2022, Google sponsored open-source hardware projects using GlobalFoundaries 180nm MCU (microcontroller) process on multi-project wafers. PIC) are using this technology because it is typically low cost and does not require upgrading of existing equipment.
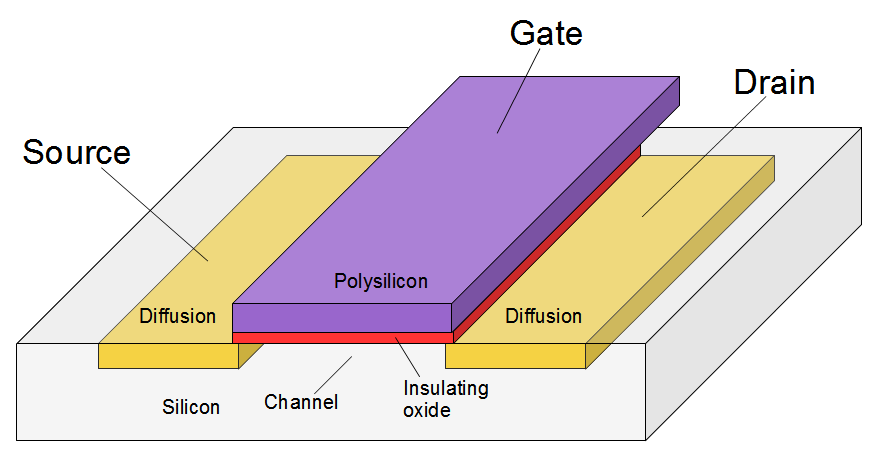
Some more recent microprocessors and microcontrollers (e.g. This was the first technology using a gate length shorter than that of light used for contemporary lithography, which had a wavelength of 193 nm. Some of the first CPUs manufactured with this process include Intel Coppermine family of Pentium III processors. The naming is formally determined by the International Technology Roadmap for Semiconductors (ITRS).

The origin of the 180 nm value is historical, as it reflects a trend of 70% scaling every 2–3 years. The 180 nm process is a MOSFET ( CMOS) semiconductor process technology that was commercialized around the 1998–2000 timeframe by leading semiconductor companies, starting with TSMC and Fujitsu, then followed by Sony, Toshiba, Intel, AMD, Texas Instruments and IBM.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
